FIRE SYSTEMS CABLES – NBR 17240
Fire system cables – with and without shielding
INNOVCABLE FIRE ALARM SB – 300V – NBR 17240
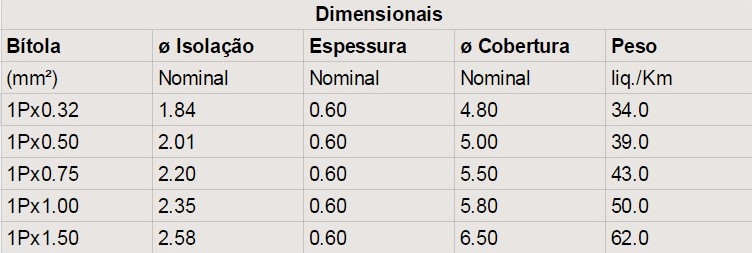
1) Stranded conductor formed by bare electrolytic copper wires, soft temper, class 2 NBR NM 280 stranding
2) Insulation in thermoplastic compound based
on polyvinyl chloride (PVC/A) 70° C.
3) Assembly of conductors in pairs or tender.
Pair: Black / Red.
Suit: Black / Red / White.
4) Twist pitch: 50 to 65mm
5) Polyester tape separator.
6) Cover in thermoplastic compound based on polyvinyl chloride (PVC/A) in Red.
• Insulation voltage: 300V – NBR 6148
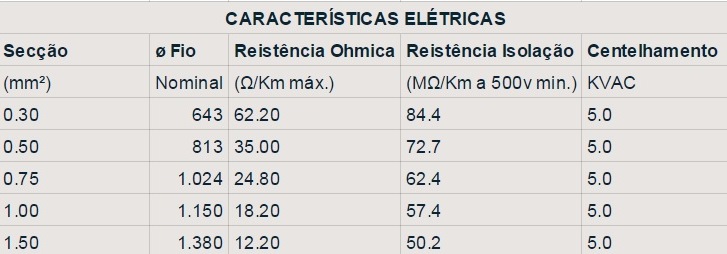
• Routine tests:
Electrical resistance of the conductor at 20ºC
Electrical voltage in Alternating Current
Insulation resistance.
Identification
INNOVCABLE FIRE ALARM SB XX mm² 300V NBR 17240 OF:XXXX/YEAR.
Applicable Specifications
Applications
Fire cable used in fixed fire alarm system facilities in conducting analog (4 - 20MA) and digital signals, point -to -point instrumentation, HART ® protocol, various sensor and meters, conventional and electronic relay feed, in general industrial environments related to systems and fire detection and alarm, security system, distance measuring systems, distance systems, distance system and emergency lighting systems.
Fire Alarm SB 300V fire cable are recommended for installation continues with galvanized steel pipes. Constructed cable to meet NBR 17240.
Excellent flexibility, resistance to chemicals, humidity and UV rays, antichama and self-extinguishable meeting the vertical propagation tests of the flame, according to NBR IEC 60332-3-23, category B.
Maximum Conductor Temperature
Conductor temperature in continuous operation: 70ºC (PVC/A)
– Can be made with other insulation:
Vein insulation material / other temperatures:
PVC/E – 105ºC
XLPE – 125 ºC or 90 ºC
HEPR – 90 ºC
Notes
Fire cable:
We can manufacture other settings on request:
1- Copper conductor tinned.
Class 1, 4 or 5 of stringing.
Court training.
2- Different sections and amount of veins.
3- Veins insulation material/other temperatures:
PVC/E -105ºC
XLPE- 125 ° C or 90 ° C
HEPR- 90 ° C
PE- 80 ° C
4- Fire cable coverage Material:
PE
PVC/ST1
PVC/ST2
PVC resistant resistant oleos, greases and other chemicals.
LSZH (non-halogenated polyolephinic compound)
5- Perfectly cylindrical coverage for cable press applications in classified areas (Ex)
6- Isolation voltage: 300V, 750V or 0.6/1kV.
InnovCable reserves the right to change this catalog without any notice.
INNOVCABLE FIRE ALARM SB – 600V – NBR 17240
1) Stranded conductor formed by bare electrolytic copper wires, soft temper, class 2 NBR NM 280 stranding
2) Insulation in thermoplastic compound based
on polyvinyl chloride (PVC/A) 70° C.
3) Assembly of conductors in pairs or tender.
Pair: Black / Red.
Suit: Black / Red / White.
4) Twist pitch: 50 to 65mm
5) Polyester tape separator.
6) Cover in thermoplastic compound based on polyvinyl chloride (PVC/A) in Red.
• Insulation voltage: 600V – NBR 6148
• Routine tests:
Electrical resistance of the conductor at 20ºC
Electrical voltage in Alternating Current
Insulation resistance.
Identification
INNOVCABLE FIRE ALARM SB XX mm² 600V NBR 17240 OF:XXXX/YEAR.
Applicable Specifications
Applications
The fire cable is used in fixed facilities of fire alarm systems in conducting analog (4 - 20MA) and digital signals, point -to -point instrumentation, Hart ® protocol, conventional and electronic relay and meters power, in general industrial environments related to systems and fire detection and alarm, measurement system, measurement systems, distance and emergency lighting systems.
Fire Alarm SB 600V fire cable is recommended for installation continues with galvanized steel pipes. Constructed cable to meet NBR 17240.
Excellent flexibility, resistance to chemicals, humidity and UV rays, antichama and self-extinguishable meeting the vertical propagation tests of the flame, according to NBR IEC 60332-3-23, category B.
Maximum Conductor Temperature
Conductor temperature in continuous operation: 70ºC (PVC/A)
– Can be made with other insulation:
Vein insulation material / other temperatures:
PVC/E – 105ºC
XLPE – 125 ºC or 90 ºC
HEPR – 90 ºC
Notes
We can manufacture on request Other Settings Fire Cable:
1- Copper Driver.
Class 1, 4 or 5 of stringing.
Court training.
2- Different sections and amount of veins.
3- Veins insulation material/other temperatures:
PVC/E -105ºC
XLPE- 125 ° C or 90 ° C
HEPR- 90 ° C
PE- 80 ° C
4- Fire cable coverage Material:
PE
PVC/ST1
PVC/ST2
PVC resistant resistant oleos, greases and other chemicals.
LSZH (non-halogenated polyolephinic compound)
5- Perfectly cylindrical coverage for cable press applications in classified areas (Ex)
6- Isolation voltage: 300V, 750V or 0.6/1kV.
InnovCable reserves the right to change this catalog without any notice.
INNOVCABLE FIRE ALARM BF – 300V – NBR 17240
1) Stranded conductor formed by bare electrolytic copper wires, soft temper, class 2 NBR NM 280 stranding
2) Insulation in thermoplastic compound based
on polyvinyl chloride (PVC/E) 105° C.
3) Assembly of conductors in pairs or tender.
Pair: Black / Red
Suit: Black / Red / White
4) Twist pitch: 50 to 65mm
5) Separator in polyester tape and collective shielding in aluminized polyester tape, with flexible drain conductor of 0.5 mm² section, formed by tinned electrolytic copper wires.
6) Cover in thermoplastic compound based on polyvinyl chloride (PVC/ST1) in Red.
• Insulation voltage: 300V – NBR 6148
• Routine tests:
Electrical resistance of the conductor at 20ºC
Electrical voltage in Alternating Current
Insulation resistance.
Identification
INNOVCABLE FIRE ALARM BF XX mm² 300V 105°C NBR 17240 OF:XXXX/YEAR.
Applicable Specifications
Applications
The fire cable is used in fixed facilities of fire alarm systems in conducting analog (4 - 20MA) and digital signals, point -to -point instrumentation, Hart ® protocol, conventional and electronic relay and meters power, in general industrial environments related to systems and fire detection and alarm, measurement system, measurement systems, distance and emergency lighting systems.
Fire Alarm 300V Fire Fire Cable is recommended for cases where excellent levels of protection against external electromagnetic interference are required, and maximum immunity against the emergence of “CrossStalk” (diaphony) among the various pairs/tender, providing their electric discharge. Constructed cable to meet NBR 17240.
Excellent flexibility, resistance to chemicals, humidity and UV rays, antichama and self-extinguishable meeting the vertical propagation tests of the flame, according to NBR IEC 60332-3-23, category B.
Maximum Conductor Temperature
In continuous regime: 105ºC (PVC/E)
– Can be made with other insulation:
Vein insulation material / other temperatures:
PVC/A -70ºC
XLPE – 125 ºC or 90 ºC
HEPR – 90 ºC
PE – 80 ºC
Notes
We can manufacture on request Other Settings Fire Cable:
1- Copper Driver.
Class 1, 4 or 5 of stringing.
2- Different sections and amount of veins.
3- Veins insulation material/other temperatures:
PVC/A -70ºC
XLPE- 125 ° C or 90 ° C
HEPR- 90 ° C
PE- 80 ° C
4- Fire cable coverage Material:
PE
PVC/E
PVC/ST2
PVC Resistant oil, greases and other chemicals.
LSZH (non-halogenated polyolephinic compound)
5- Perfectly cylindrical coverage for cable press applications in classified areas (Ex)
6- Isolation voltage: 600V, 750V, 0.6/1kV among others.
Innovcable reserves the right to change this catalog without prior notice.
INNOVCABLE FIRE ALARM BF – 600V – NBR 17240
1) Stranded conductor formed by bare electrolytic copper wires, soft temper, class 2 NBR NM 280 stranding
2) Insulation in thermoplastic compound based
on polyvinyl chloride (PVC/A) 70° C.
3) Assembly of conductors in pairs or tender.
Pair: Black / Red.
Suit: Black / Red / White.
4) Twist pitch: 50 to 65mm
5) Separator in polyester tape and collective shielding in aluminized polyester tape, with flexible drain conductor of 0.5 mm² section, formed by tinned electrolytic copper wires.
6) Cover in thermoplastic compound based on polyvinyl chloride (PVC/E) 105° C in red.
• Insulation voltage: 600V – NBR 6148
• Routine tests:
Electrical resistance of the conductor at 20ºC
Electrical voltage in Alternating Current
Insulation resistance.
Identification
INNOVCABLE FIRE ALARM BF XX mm² 600V 70°C NBR 17240 OF:XXXX/YEAR.
Applicable Specifications
Applications
The fire cable is used in fixed facilities of fire alarm systems in conducting analog (4 - 20MA) and digital signals, point -to -point instrumentation, Hart ® protocol, conventional and electronic relay and meters power, in general industrial environments related to systems and fire detection and alarm, measurement system, measurement systems, distance and emergency lighting systems.
Fire Alarm BF 600V Fire Cable is recommended for cases where excellent levels of protection against external electromagnetic interference are required, and maximum immunity against the emergence of “CrossStalk” (diaphony) among the various pairs/tender, providing their electric discharge. Constructed cable to meet NBR 17240.
Excellent flexibility, resistance to chemicals, humidity and UV rays, antichama and self-extinguishable meeting the vertical propagation tests of the flame, according to NBR IEC 60332-3-23, category B.
Maximum Conductor Temperature
Continuous conductor temperature: 70ºC (PVC/A)
External jacket temperature: 105ºC (PVC/E).
– Can be made with other insulation:
Vein insulation material / other temperatures:
PVC/A -70ºC
XLPE – 125 ºC or 90 ºC
HEPR – 90 ºC
PE – 80 ºC
Notes
We can manufacture on request Other Settings Fire Cable:
1- Copper Driver.
Class 1, 4 or 5 of stringing.
Court training.
2- Different sections and amount of veins.
3- Veins insulation material/other temperatures:
PVC/E -105ºC
XLPE- 125 ° C or 90 ° C
HEPR- 90 ° C
PE- 80 ° C
4- Fire cable coverage Material:
PE
PVC/ST1
PVC/ST2
PVC resistant resistant oleos, greases and other chemicals.
LSZH (non-halogenated polyolephinic compound)
5- Perfectly cylindrical coverage for cable press applications in classified areas (Ex)
6- Isolation voltage: 300V, 750V or 0.6/1kV.
InnovCable reserves the right to change this catalog without any notice.
Research and Knowledge Centers
In order to stand out and lead through state -of -the -art research, InnovCable closely follows the advances and innovations developed by important centers of excellence and research in the electricity sector, with special attention to the area of cables, both in Brazil and in the international scenario.
Next, we present some of the main centers of knowledge that are a reference for our work:
Innovcable Knowledge Bases
- Knowledge Academy: Application and Installation of Moveable Cables - Rolante Bridge, Currency, Festoons, Elevators, Crane Treadmills…
- InnovCable Furniture Guide: What mobile cables do you use?
- Why use InnovCable Mobile Cables: Considerations of why utilize mobile cables
- Cable storage and transportation guidelines
- GLOSSARY: Technical Terms in English
- Color Code Tables: According to DIM47100, BS4737, BS5308
- Copper Temperature Coefficients: Constant to convert resistance at various temperatures to the standard 20 ° CE reference temperature of constants to convert resistance to 20 ° C other temperatures.
- MISCELLANEOUS METAL DATA
- Tables: Cenelec - VDE
- Dimensioning tables: power cables - NBR 5410
- COMPENSATION AND EXTENSION THERMOCOUPLE CABLES AND WIRE TABLES
- Driver Class : mm² x AWG
- Diverse technical information
- Naval cable codes and nomenclatures as per Nek606
- SHF1 AND SHF2 COVERS ACCORDING TO NEK-606
- Resistance of insulation and cover materials, comparative of properties
- Resistance from Armação / Armor Resistance
- Current classifications and voltage drop vol 1 - IEE
- Current classifications and voltage drop Vol 2 - IEE
- Fire Performance Standards: Fire Performance Cable Standards
- Radius of minimum allowed curvature: according to DIN VDE 0298 PART 3
- STANDARDS
- Voltage Fall Calculations: VoltaGe Drop Calculations
Databases and academic search mechanisms
- IEEE Xplore Digital Library: IEEE
- ACM Digital Library: ACM
- ScienceDirect: SCIENCE DIRECT
- Scopus: SCOPUS
- CAPES Journal Portal: CAPES
- Google Scholar: GOOGLE SCHOLAR
Prominent journals and journals
- IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS: (Available through IEEE XPLORE)
- IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY: (Available through IEEE XPLORE)
- IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS: (Available through IEEE XPLORE)
- Telecommunications Magazine (Inatel): INATEL
- Control & Automation Magazine (SBA): SBA
- Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ): DOAJ
Institutional repositories and research groups
- Brazilian Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations (BDTD): BDTD
- GEPOC – Power Electronics and Control Group (UFSM): GEPOC
Technical standards entities
These organizations are responsible for developing and publishing the standards that guarantee the safety, quality and interoperability of electrical cables and communication.
- ABNT (Brazilian Association of Technical Standards): It is the National Forum of Standardization in Brazil. ABNT standards, such as NBR 5410 (low voltage electrical installations), are fundamental for any project in the country.
- ABNT
- To consult the collection: ABNT COLLECTION
- IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission): The International Electrical Commission is the world leading organization in the elaboration and publication of international standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies. Many ABNT standards are based on IEC standards.
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization): Although it is a standardization organization for a wide range of industries, ISO also publishes relevant rules for the cable sector, especially related to Quality Management Systems (ISO 9001).
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories): A global security science organization, well known for its product certifications. UL standards are an important security reference, especially for products for the US market.
- Aunt (Telecommunications Industry Association): Main Association for the Information and Communication Technology Industry (ICT). Develops structured cabling standards, such as the ASI/TIA-568 series, which are a world reference for communication networks.
Associations, unions and regulatory entities
These organizations represent the interests of industry, promote quality and regulate the sector.
- Anatel (National Telecommunications Agency): It is the regulator of the telecommunications sector in Brazil. Anatel is responsible for approving and certification of telecommunications products, including network cables and fiber optics.
- Sindicel (Union of the Industry of Electrical Driver, Treflation and Lamination of Non -Ferrous Metals of the State of São Paulo): It represents industries in the sector, acting in defense of their interests and promoting actions to combat the illegal cable market.
- Qualifio (Brazilian Association for the Quality of Electric Wires and Cables): Entity that monitors the quality of the electricized wires and cables sold in Brazil, maintaining a list of approved and non -compliance manufacturers.
- Abinee (Brazilian Association of Electric and Electronic Industry): It represents the electrical and electronic sectors nationally, acting on several fronts, including standardization and regulation issues.
- BICSI: A global professional association that supports the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) community. Provides education, certifications and publications of standards for design and installation of cabling systems.
- International Cablemakers Federation (ICF): Global Forum that brings together the CEOs of the world's leading wire and cable companies to discuss industry trends and challenges.
Research Giants: Ponta Universities in Brazil in the area of Electric Cables and Communication
Brazil has a robust ecosystem of public universities that are true references in research and development in the areas of electrical and communication engineering. Several of them house state -of -the -art laboratories and international recognition research groups that act directly with power cable themes, optical fibers, dielectric materials and communication systems.
Next, we highlight some of the top first -line universities and their respective centers of excellence on the subject:
1. State University of Campinas (Unicamp)
Main focus: Optical and photonic communications
Considered one of the largest telecommunications innovation centers in Latin America, Unicamp, especially through its Faculty of Electrical and Computing Engineering (FEEC) and the Gleb Wataghin Institute of Physics (IFGW), is an absolute leader in optical fiber research and communication systems. Proximity and historical collaboration with CPQD (Telecommunications Research and Development Center) solidifies its position.
- Laboratories and prominent groups:
- Optical and Microwave Communications Laboratory (Lapcom): Focused on research of optical amplifiers, doped fibers and electromagnetic wave propagation.
- Integrated Photonic Laboratory (LIF): It brings together various laboratories and researchers for the development of photonic devices, special optical fibers and communication systems.
- Group of ultra -rarefilled phenomena and optical communications (gfurco): Performs advanced studies on optical fibers, devices and phenomena at very high transmission speeds.
2. Federal University of Itajubá (Unifei)
Main focus: power systems and high voltage
Unifei is a historical reference and of great prestige in electrical power systems in Brazil. Its Institute of Electrical and Energy Systems (ISEE) is one of the most important in the country, with strong performance in studies involving power cables, electrical insulation and energy transmission.
- Laboratories and prominent groups:
- High voltage laboratory (lat-efei): One of the most renowned in the country, performs tests and high voltage tests on cables, insulators and other electrical systems equipment. It is pioneering and fundamental for the development of the national electricity sector.
- Link: LAT-EFEI
- Institute of Electrical and Energy Systems (ISEE): It brings together various laboratories and research groups in areas such as system protection, energy quality and automation, all intrinsically linked to the performance and application of electrical cables.
- High voltage laboratory (lat-efei): One of the most renowned in the country, performs tests and high voltage tests on cables, insulators and other electrical systems equipment. It is pioneering and fundamental for the development of the national electricity sector.
3. University of São Paulo (USP)
Main focus: power systems, power electronics and telecommunications
USP, with its multiple campuses, has extremely strong and diverse research. Both the Polytechnic School (POLI-USP) in São Paulo and the São Carlos School of Engineering (EESC-USP) have excellence laboratories and research groups that work on cable related topics.
- Laboratories and prominent groups:
- High voltage laboratory (EESC-USP): Located in São Carlos, it works in the study of high voltage phenomena, insulating materials and electrical discharges.
- EESC-USP (See LAT in the list)
- Research Laboratory in Electrical Systems Protection and Automation (POLI-USP): Develops research in electrical systems protection, where modeling and cable behavior in absences are essential.
- Telecommunications Laboratory (EESC-USP): With groups dedicated to microwave and optics, develops research relevant to the communication cables area.
- EESC-USP (See TELECOM in the list)
- High voltage laboratory (EESC-USP): Located in São Carlos, it works in the study of high voltage phenomena, insulating materials and electrical discharges.
4. Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC)
Main focus: power electronics and energy systems
UFSC is a hub of excellence recognized worldwide in power electronics. Developed research is crucial for cable application to energy conversion systems, engines and renewable sources connection.
- Laboratories and prominent groups:
- Institute of Power Electronics (INEP): One of the most productive research groups in the world in the area. Develops state -of -the -art technology for converters and power inverters, which connect through cables to various loads and sources.
5. Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG)
Main focus: Telecommunications and Applied Electromagnetism
UFMG has a consolidated postgraduate program in Electrical Engineering, with research groups relevant to the area of communication and electromagnetism, which give the theoretical and applied base for the development of cable and wave guides technologies.
- Laboratories and prominent groups:
- Department of Electronic Engineering (DELT): It has research laboratories in telecommunications and networks, where it is studied from fiber optic communication to wireless communication systems, which often depend on a robust wable infrastructure.
Research Institutes
National scenario
1. CPQD (Telecommunications Research and Development Center) - Brazil
Main focus: Information and Communication Technologies (ICT)
Headquartered here in Campinas, CPQD is the largest ICT Research Institute in Latin America and a key piece in the history of Brazilian telecommunications. It develops from optical component technology to full software and hardware platforms for 5G/6G networks, IoT and cyber security. For a communication engineer, it is a mandatory reference.
- Relevant areas and platforms:
- Optical communications: Poor research on photonic devices, special optical fibers and high capacity transmission systems.
- Wireless connectivity: Systems development and testing for 5G, 6G and Open Ran.
- Validation and tests: Accredited laboratories for testing and equipment certification, including cables and components, for compliance with Anatel standards.
2. CEPEL (Electricity Research Center) - Brazil
Main focus: generation, transmission and distribution of electricity
CEPEL is the research arm of the Eletrobras Group and the largest electrical research institute of the southern hemisphere. Its performance is vital to the safety and evolution of the National Interconnected System (SIN). CEPEL research on high voltage equipment, materials and systems have a direct impact on the specifications and operation of power cables.
- Areas and prominent groups:
- EQUIPMENT AND MATERIAL LABORATORY (LEM): Performs high voltage tests and high current in cables, transformers and other active electrical system.
- Link: CEPEL LEM
- Transmission Technologies: Research applied on transmission lines, substations and high voltage equipment, including cable behavior under extreme conditions.
- EQUIPMENT AND MATERIAL LABORATORY (LEM): Performs high voltage tests and high current in cables, transformers and other active electrical system.
3. Inmetro (National Institute of Metrology, Quality and Technology) - Brazil
Main focus: scientific and industrial metrology, compliance assessment
Although first a regulatory and metrology entity, Inmetro has very high level laboratories that conduct research to establish the country's measurement standards. Its scientific metrology and technology board is critical to ensuring that rehearsals in cables and other products are accurate and reliable throughout Brazil.
- Areas and prominent groups:
- Electric Metrology Laboratory (Label): Responsible for maintaining and disseminating national standards for electrical quantities, base for all cable tests.
- Link: INMETRO LABEL
- Electric Metrology Laboratory (Label): Responsible for maintaining and disseminating national standards for electrical quantities, base for all cable tests.
International scenario
1. Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft-Germany
Main focus: Applied research in multiple areas of engineering
Fraunhofer society is the largest applied research organization in Europe, with 76 institutes scattered throughout Germany. Each institute has a specific focus, and several are world references in the areas of communication and energy.
- Prominent institutes:
- FRAUNHOFER INSTITUTE FOR TELECOMMUNICATIONS (Heinrich Hertz Institute - HHI): World leader in fiber optic networks, photonic components, video compression (creators of patterns such as H.264/stroke and H.265/HEVC) and wireless communication.
- Link: HHI Fraunhofer
- FRAUNHOFER INSTITUTE FOR ENERGY ECONOMICS AND ENERGY SYSTEM TECHNOLOGY (IEE): Focused on energy transition, develops technology for renewable integration, smart networks and stability of power systems.
- Link: IEE Fraunhofer
- FRAUNHOFER INSTITUTE FOR TELECOMMUNICATIONS (Heinrich Hertz Institute - HHI): World leader in fiber optic networks, photonic components, video compression (creators of patterns such as H.264/stroke and H.265/HEVC) and wireless communication.
2. NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) - USA
Main focus: science of measurement, standards and technology
North American equivalent of Inmetro, but with an even more comprehensive performance in fundamental and applied research. The NIST is crucial for US technological development, creating standards and measurement technologies that allow innovation throughout the industry.
- Laboratories and prominent groups:
- Communications Technology Laboratory (CTL): Develops fundamental research in metrology for 5G/6G networks, network resilience and quantum communication.
- Material Measurement Laboratory (MML): Conducts research on material properties, including polymers used in cable isolation and advanced electronics materials.
3. NIC (National Institute of Information and Communications Technology) - Japan
Main focus: Information and Communication Technologies
NICT is Japan's main public research institute in the ICT area. It is known for its record -compliance with fiber optic transmission, having shown the highest transmission rates in the world on several occasions, as well as strong research on quantum and security networks.
- Prominent groups and initiatives:
- Photonic Network System Laboratory: Research Ultra-High Capacity Optical Transmission Systems, exceeding the boundaries of what is possible in a single optic cable.
4.
Main focus: microelectronics, nanotechnology and photonic in silicon
Leti is an institute of the Commissioner of Atomic Energy and Alternative Energy (CEA) of France and a global leader in miniaturization of technologies. They are pioneers in “photonic silicon”, which seeks to integrate optical components directly into silicon chips, a revolution for short and medium distance communications.
- Prominent groups and initiatives:
- Optics and Photonics Division: Develops from image sensors to optical communication systems and dealing integrated in chips, impacting the future of communication cables on data centers and high performance computing.
These institutions represent the forefront of academic research in the sector, training highly qualified professionals and developing technology that drives the entire cable industry.