THERMOCOUPLE CABLES
Standards / Colors / Standard and Special Types / Definitions/ Construction Characteristics
THERMOCOUPLE CABLES
1-) Formation: from 1 to 36 pairs, gauges from 32 AWG to 16 AWG, stringing according to class 5, solid wire, flexible cable.
2-) Without shielding: Individual insulation of the PVC, PTFE, INNOVDF or Silicone conductor. General insulation of PVC, Silicone, fiber or INNOVDF conductors.
3-) With collective shielding: Individual insulation of the conductor in PVC, PTFE, INNOVDF or Silicone, b electrostatic shielding with aluminized polyester tape applied. helically with 100% overlap in the set of pairs with 20AWG tinned copper drain, Total insulation of conductors in PVC, PTFE, INNOVDF, Silicone or Fiberglass.
4-) With individual shielding: Individual insulation of the PVC, PTFE, INNOVDF or Silicone conductor, b electrostatic shielding with aluminized polyester tape applied. helically with 100% overlap, together with the drain in the pair in 20 AWG gauge tinned copper, general insulation of conductors in PVC, Silicone, Fiberglass, PTFE or INNOVDF.
5-) With individual and collective shielding: Individual insulation of the PVC, PTFE, INNOVDF or Silicone conductor, b electrostatic shielding with aluminized polyester tape applied helically with overlap of 100% covering on the pair, together with the drain cable on the pair of 20 AWG gauge tinned copper and collective shielding on all pairs in aluminized polyester tape applied helically with overlapping 100%, general insulation of PVC, PTFE, INNOVDF, Silicone or Fiberglass conductors.
Extension/Compensation Cables for Thermocouples
– Standardized types: single pairs / multipairs – 01 to 36 pairs.
– Gauges: 1.5mm2 – 16 AWG – 1mm2 – 18 AWG – 0.75mm2 – 20 AWG – 0.5mm2
1- Rigid conductor (monofilare)
2- Flexible conductor (multi-strand)
3- Insulation: colors in accordance with standards.
4- Pair brought together in parallel.
5- Twisted pair with pitch 50 ± 10mm.
6- Pairs numbered correlatively from number 1 to the total number of pairs.
7- Individual electrostatic shielding (per pair): Aluminum/mylar tape, applied helically with overlap (100% coverage)
7a- Individual shield drain: Continuity/earth conductor, copper
tinned, flexible, in permanent contact with the aluminized part of the tape.
8- Anti-hygroscopic shielding: Mylar tape wrapping, applied helically with overlap (100% coverage)
9- Collective electrostatic shielding (total to the set): Aluminum/mylar tape, applied helically with overlap (100% coverage).
9a- Collective shield drain: Continuity/earth conductor, copper
tinned, flexible, in permanent contact with the aluminized part of the tape.
10- Communication conductor, made of copper, flexible, insulated with the requested material, to facilitate installation.
11- Inner cover: isolated with requested material
12- Armor: galvanized steel mesh, or two flat strips of galvanized steel, applied in an open helicoid, with the 2nd strip covering, with
overlap, the interval between successive turns of the first.
13- External cover: isolated with requested material. Colors in accordance with standards.
Note: TERMOINNOV standardized types are manufactured in compliance with ISA/ANSI identification/calibration. However, if desired, they can be
provided under other standards, as well as other constructions may be provided.
Identification
ISA/ANSI standard
1-) SINGLE COUPLES – STANDARDIZED CONSTRUCTIONS:
SB / WITHOUT SHIELDING
B / Parallel Rigids
A / Parallel Flexibles
1A – R / Twisted Rigids
1A – F / Twisted Flexibles
BT / COLLECTIVE SHIELDING
1B – R / Twisted Rigids
1B – F / Twisted Flexibles
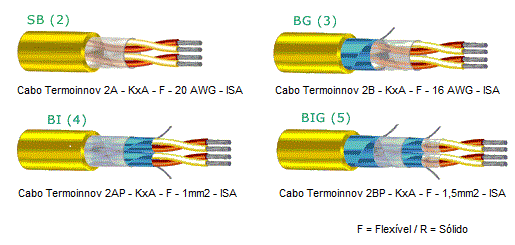
2-) MULTIPAIRS – STANDARDIZED CONSTRUCTIONS:
A – SB / Without Shielding
AP – BI / Individual Shielding
B – BG / General Armor
BP – BIG / Individual and General Armor
F – BG / FA /General Armor with frame (steel tape)
FP – BIG / FA /Individual and general armor with frame
Applicable Specifications
Technical Definitions:
a) Wires are those conductors made up of a solid shaft, and Cables are those made up of a bundle of smaller diameter conductors, forming a flexible conductor.
b) Wires and Extension Cables, are conductors manufactured with the same alloys as the thermocouples for which they are intended; therefore, they present the same FEM x temperature curve (up to a temperature limit).
The wires and extension cables are used with metal-based or basic thermocouples types T, J, E, K and N. Despite having the same alloy as the thermocouples, they have a lower cost due to the limited temperature they can be subjected to, because its chemical composition is not as homogeneous as that of the thermocouple.
c) Compensation Wires and Cables, are conductors manufactured with alloys different from the thermocouples for which they are intended, but also presenting the same FEM x temperature curve as the thermocouples (up to a temperature limit).
Compensation wires and cables are mainly used with noble thermocouples (made from platinum) types S and R, however they can be used in some basic thermocouples and with new types that are not yet standardized.
The table below indicates the color code, working range and tolerances of wires and extension and compensation cables for American, German (the most used), English, Japanese, French and Brazilian standards.
Although this table is well known and used worldwide, we present the color table, the new table of temperature ranges, errors and color code according to IEC-584-3 of 1989.
According to this international standard IEC-584-3, it was adopted in several countries around the world, including adopted by ABNT, becoming an NBR, the new tolerances, working ranges and color code for extension and compensation wires and cables.
This standard adopted that the suffix “X” for cable types refers to extension wires and cables and the suffix “C” to compensation wires and cables. The letters “A” or “B” refer to different types of alloys.
Applications
– The color codes marked with the symbol refer only to the SX type.
– Due to the non-linearity of the FEM x Temperature curves of type S, R, B thermocouples, the error introduced into the system by the compensation wire or cable will be variable when expressed in degrees. Therefore the error limits are based on the following measuring junction temperatures:
SX / RX = Greater than 870ºC
BX = Greater than 1000ºC
– WX and VX wires or cables for type K thermocouple were excluded from ANSI MC 96.1 of 1982.
– Reference junction at 0ºC.
Termoinnov wires and cables are used as extension wires and cables for thermocouples types T, J, K, E, and compensation for thermocouples types S, B, making the interconnection between the sensor and the instrument. Colors, temperature limits, accuracy, are found in the presentation table.
Maximum Conductor Temperature
- a) The temperature range in some cases must be smaller than those shown in the table due to the limitation of wire or cable insulation.
- b) The cables used for type B thermocouple are common copper conductors.
In a range of 0 to 100ºC the maximum deviation is ±40uV (±3.5ºC) with a measuring junction temperature of 1400ºC.
The insulation used in extension and compensation wires and cables must be chosen in such a way as to resist the conditions of the environment where it will work, taking into account all variables such as temperature, mechanical stress, humidity, abrasion, presence of oil and other components.
Due to the wide variety of applications, extension and compensation wires and cables can be supplied with different types of external and internal insulation.
PVC -20 AT 80ºC
ASBESTOS 25 TO 500ºC
FIBER 20 AT 270ºC
SILICONE -60 TO 250ºC
PTFE -100 TO 260ºC
PVDF -55 to 145ºC
Notes
– We can produce, upon request, several other options and cable configurations. Innovcable reserves the right to change this catalog without prior notice.